TEETH INJURIES
 |
 |
 |
Types of Teeth Injuries
- Loosened Tooth: If mild, it usually tightens up on its own (may bleed a little from the gums).
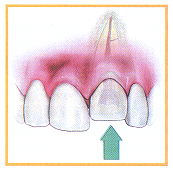
- Displaced Tooth: Any tooth that has been pushed out of normal position (displaced) needs to be seen by a dentist to assess the damage. Displaced teeth that interfere with biting, chewing, or closing of the mouth need to be repositioned within 4 hours for reasons of comfort and function. Mild displacement can wait for 24 hours for assessment.
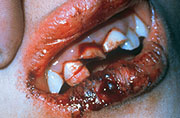
- Knocked-out Tooth: This is a dental emergency. The knocked-out tooth needs to be placed back in its socket at soon as possible, ideally within one hour.
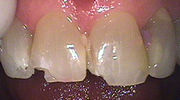
- Chipped or Fractured Tooth: All need to seen by a dentist. A fracture that enters into the pulp (center) of a tooth is referred to as complicated; the tooth is usually painful or sensitive to hot and cold. You may be able to identify a complicated tooth fracture by noticing a small red dot or pink blush (the pulp) in the fractured area. To prevent permanent tooth damage, fractures into the pulp need to be treated within 3-4 hours.
FIRST AID for Knocked-out Tooth
- To save the tooth, it must be put back in its socket as soon as possible (2 hours is the outer limit for survival). Use the following technique:
- Rinse off the tooth with saliva or water. Do not scrub the tooth.
- Replace it in the socket facing the correct way.
- Press down on the tooth with your thumb until the crown is level with the adjacent tooth.
- Lastly, bite down on a wad of cloth to stabilize the tooth until you can be seen by a dentist.
Transporting a Knocked-out Tooth
- Follow these instructions if you are not able to put the tooth back in its socket.
- It is very important to keep the tooth moist. Do not let it dry out.
- Transport the tooth in saliva or milk.
WHEN TO CALL YOUR DOCTOR FOR TOOTH INJURY
Call 911 Now (you may need an ambulance) If
- Knocked out (unconscious)
- Major bleeding that can't be stopped
Call Your Dentist Now (night or day) If:
- You think you have a serious injury
- Knocked-out tooth (see First Aid and Transport information)
- Tooth is almost falling out
- Tooth is greatly pushed out of its normal position
- Tooth that's pushed out of its normal position interferes with normal bite
- Chipped tooth is missing a large piece, or a red dot is visible inside the chipped area
- Bleeding won't stop after 10 minutes of direct pressure
- Severe pain
Call Your Dentist Within 24 Hours (between 9 am and 4 pm) If:
- You think you need to be seen
- Tooth is slightly pushed out of its normal position
- Can see a chip or fracture line in the tooth
- Tooth sensitive to cold fluids
- Tooth feels very loose when you try to move it
Call Your Dentist During Weekday Office Hours If:
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home If
- Minor tooth injury and you do not think you need to be seen
HOME CARE ADVICE FOR MINOR TOOTH INJURIES
- Local Cold: For pain, apply a piece of ice or a Popsicle to the injured gum area for 20 minutes.
- Pain Medication: For pain relief with doctor's permission take acetaminophen every 4-6 hours (e.g. Tylenol; adult dosage 650 mg; 2 tablets) OR ibuprofen every 6-8 hours (e.g. Advil, Motrin; adult dosage 400 mg; 2 tablets).
- Do not take ibuprofen if you have stomach problems, kidney disease, or other contraindications to using this type of anti-inflammatory drug. Do not use if pregnant. Do not use ibuprofen for longer than 7 days without consulting your Professional Care Provider.
- Do not take acetaminophen if you have liver disease.
- Read the package instructions thoroughly on all medications that you take.
- Soft Diet: If you have any loose teeth, eat a soft diet for 3 days. After 3 days, they should be tightening up.
- Call Your Dentist If:
- Pain becomes severe
- Tooth becomes sensitive to hot or cold fluids
- Tooth becomes a darker color
- You become worse or develop any of the "Call Your Doctor" symptoms.
Disclaimer: This information is not intended be a substitute for professional medical advice. It is provided for educational purposes only. You assume full responsibility for how you choose to use this information.
Adult HouseCalls Online. Copyright © 2000-2005 David Thompson, M.D. FACEP
Reviewed 10/2005
Revised 7/2004